end tidal co2 meaning
1 ACLS guidelines define high quality chest compressions as. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 is the level of carbon dioxide that is released at the end of an exhaled breath.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
The capnogram is a direct monitor of the inhaled and exhaled concentration or partial pressure of CO 2 and an indirect monitor of the CO 2 partial pressure in the arterial blood.

. When calculating the gradient the clinician is comparing the carbon dioxide CO 2 sampled from the ABG. Mengert The New England Journal of Medicine. MONITORING of end-tidal carbon dioxide is one of the most important means of determining the physiologic well-being of anesthetized patients.
Alveolar dead space in particular is what affects the end-tidal CO 2 measurement which is taken at the end of expiration. Medical Definition of end-tidal. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45.
It is the standard of care during certain procedures such as intubations and sedations and can be used in variety of clinical situations. On average during CPR if adequate chest compressions are being delivered a cardiac index of 16-19 Lminm2 can be generated which correlates with ETCO2 pressures of 20mmHg. Multiple monitoring options so you can choose what and how to monitor respiratory status.
Like pulse oximetry before it alerting us to changes in oxygenation end-tidal CO2 monitoring or ETCO2 is rapidly becoming an additional vital sign. Bhende MS LaCovey 2001. So basically its all to do with dead space.
EtCO 2 reflects cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow as CO 2 is transported by the venous system to the right side of the heart and then pumped to the lungs by the right ventricle as well as the ventilation minute volume Paiva et al 2018. Ad View a brochure to learn about end-tidal CO2 capnography. Most medical sources define hypocapnia as less than 35 mm Hg for partial CO2 pressure in the arterial blood.
This is a major respiratory symptom. End-tidal CO 2 monitoring has also been useful for breathing retraining as it provides additional information about the. End-tidal carbon dioxide is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide EtCO 2 at the end of an exhaled breath.
Since 2001 Infinium Medical has been designing and manufacturing a wide range of leading-edge medical. Cambra. Available evidence has established that ETCO 2 measurement can provide an indication of cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow.
Low EtCO 2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion which can be caused by hypovolemia sepsis or dysrhythmias. The arterial CO2 value for normal breathing at rest is 40 mm. CO2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism which gets transported in the blood to the lungs for elimination.
Of or relating to the last portion of expired tidal air End-tidal carbon dioxide monitors are already being used and are recommended to indicate the adequacy of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and the likelihood of a successful resuscitation. We routinely use ETCO2 to provide information on ventilation. The gradient is the difference between the arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure PaCO 2 and the etCO 2 partial pressure is a result of the relationship between ventilation and perfusion or rather ventilation-perfusion matching VQ.
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. Eisenberg and Terry J.
When the measurement is taken at the end of a breath exhaling it is called end tidal CO 2 ETCO 2. In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg. In critical care End Tidal CO 2 monitoring is used to assess adequacy of circulation to the lungs which provides clues about circulation to the rest of the body.
ETCO 2 levels reflect the adequacy with which carbon dioxide CO 2 is carried in the blood back to the lungs and exhaled. End-tidal CO 2 etCO2 monitoring via capnography for example has been a valuable tool in clinical settings emergency medicine for many decades see medical reviews. Infinium Medicals end tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitor the Infinium EnTide is an affordable reliable and accurate piece of medical equipment designed to help health care professionals across the globe provide their patients with the best care possible.
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 monitoring is not a new modality in the pediatric emergency department PED and emergency department. However ETCO2 may be underused in the PED setting. Exhaled carbon dioxide both in terms of its quantity and pattern provides detailed information on the cardiopulmonary system.
End tidal carbon dioxide concentration. Definition of Low CO2 hypocapnia Hypocapnia hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia is defined as a deficiency of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood. But ETCO2 can also provide valuable information on the adequacy of cardiac perfusion.
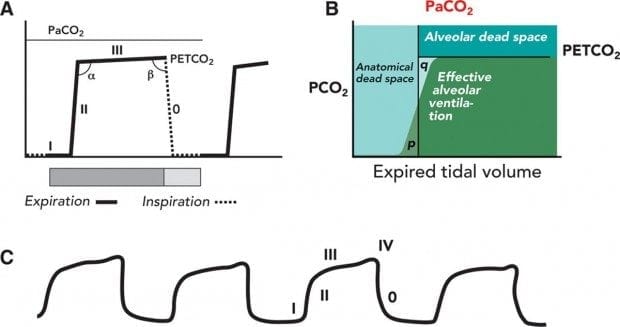
By that stage anatomical dead space has completely emptied and is.
End Tidal Co2 The Drummer Of The Vital Sign Band Pem4

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

E Learning Basics Of Capnography Youtube
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Normal And Abnormal Capnography Waveforms Infographic Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Basic Waveform Capnography As A Continuous Monitoring Tool During Mechanical Ventilation

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
The Normal Capnograph Waveform Deranged Physiology

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

